Main chiller components are Compressor, Evaporator, condenser, expansion valve, Electric panel & control panel. In this article we will discuss the purpose & working of this components one by one.
There are many different types & range of chiller but essentially they all have almost similar major components.
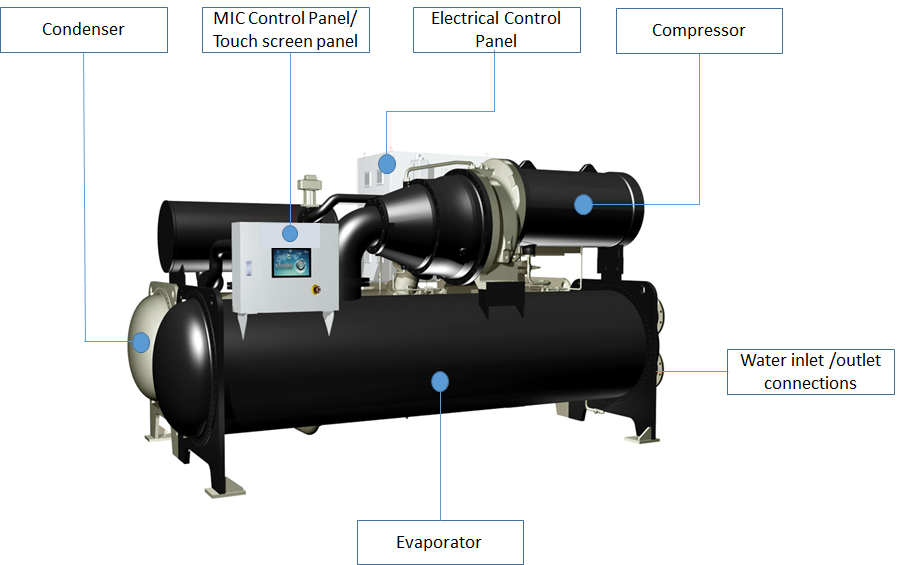
Compressor
Compressors are the most critical component in any refrigeration system. It is the prime mover attached to electric motor which compresses the refrigerant to high pressure & temperature. Once the refrigerant in a evaporator absorbs the heat from a space it becomes a gas, but it is incapable of releasing the heat right away in this form. However, after the compressor raises the pressure and temperature of the gasified refrigerant, it concentrates the heat and can be expelled through the condenser.
They also account for the most energy consumption of a system and impact efficiency. Because of their critical function, compressors represent 25-40% of total system costs. Hence selection of compressor for any chiller system is important factor, below are few different types of compressor popular in the market.
- Centrifugal compressor: Use centrifugal force to compress the refrigerant vapor. These are ideal for complex projects with large cooling loads, such as hospitals, universities or naval ships.
- Screw Compressors: Two rotors or screws tap & compress the refrigerant gas to high pressure. Screw compressors are ideal for medium to large cooling projects, such as multistory office buildings and facilities.
- Scroll compressor: Scroll compressors use one orbiting and one fixed scroll to provide continuous compression of the refrigerant. Ideal for small to medium cooling loads.
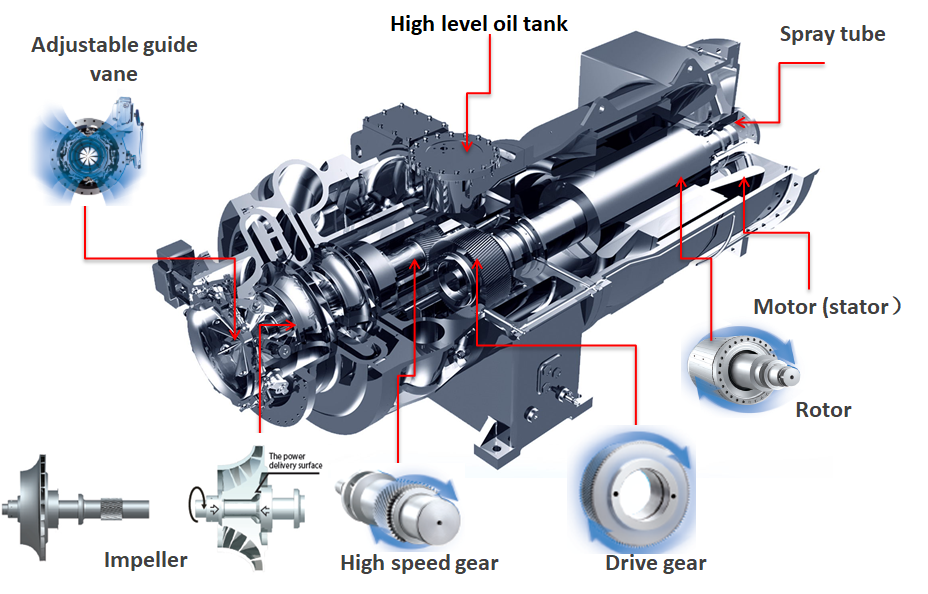
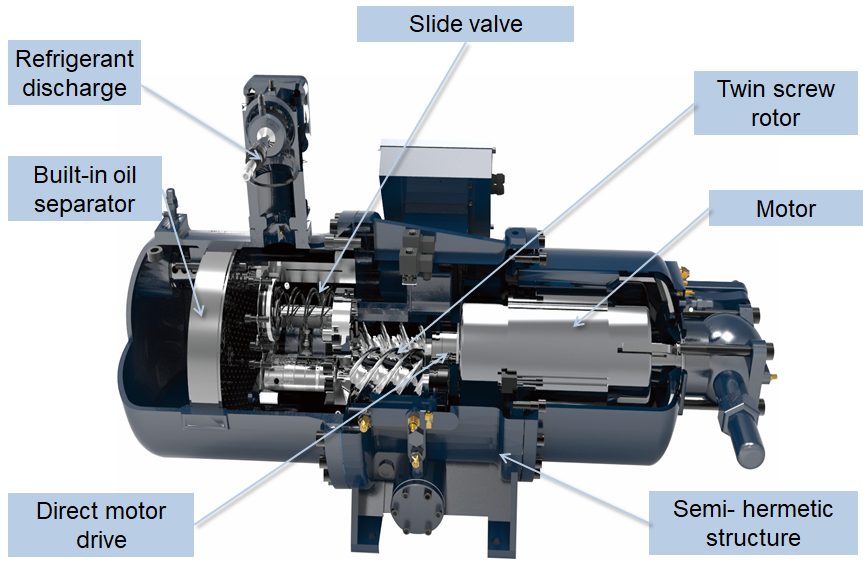
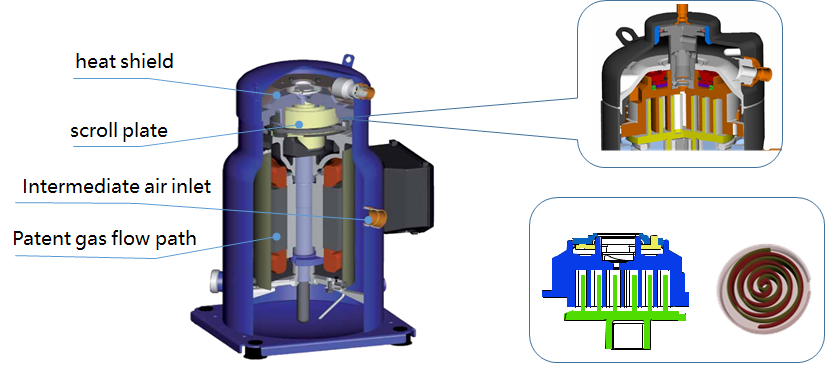
scroll compressor section
Condenser:
Condenser is placed in high pressure side of refrigeration system. Its function is to remove heat of the hot vapour refrigerant discharged from the compressor. The hot vapour refrigerant consists of the heat absorbed by the evaporator and the heat of compression added by the mechanical energy of the compressor motor. The heat from the hot vapour refrigerant in a condenser is removed first by transferring it to the walls of the condenser tubes and then from the tubes to the condensing or cooling medium. The cooling medium may be air or water or a combination of the two.
Condenser is located after the compressor & before the expansion valve. The refrigerant and the water do not mix they are kept separated by a pipe wall, the water flows inside the pipe and the refrigerant flows on the outside.
Generally Air cooled condenser consists of Finned exchanger, made from copper tubes & the aluminum fins set at a suitable distance apart to ensure maximum heat exchange efficiency. And is directly cooled by the air flow of its specific fans.
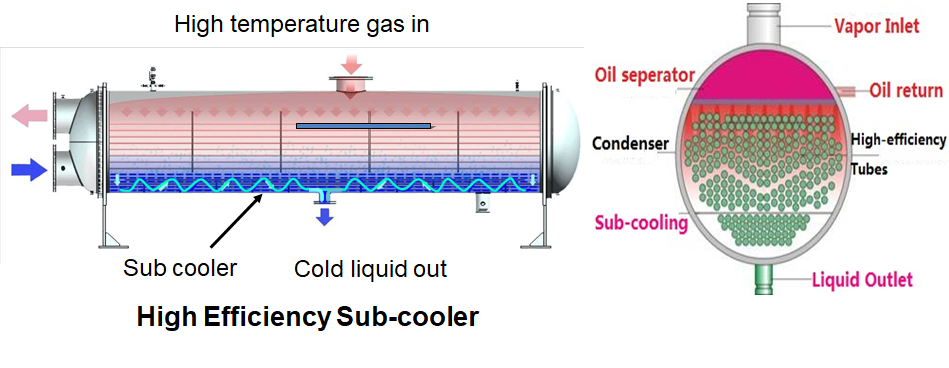
Shell & tube type Water cooled condenser are popular , made of copper tubes & Alloy steel shells (water box). The heat is rejected to the water coming out from the cooling tower & subsequently to the atmosphere via cooling tower.
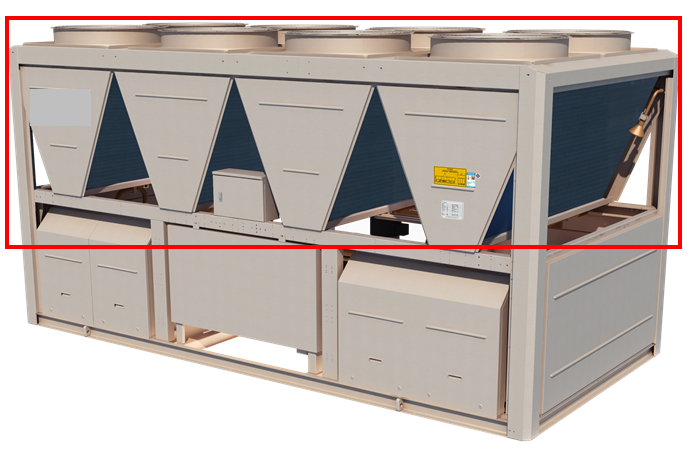

Air cooled condenser
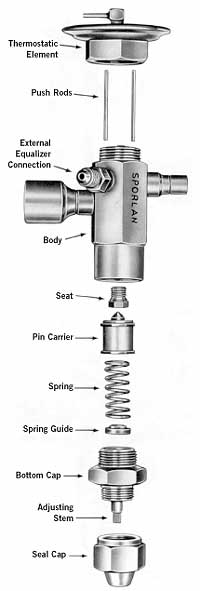
Expansion Valve:
Also known as metering device or throttling device that divides the high pressure side & low pressure side of refrigerating system. It is located between the condenser & evaporator.
- It reduces the high pressure liquid refrigerant to low pressure liquid refrigerant, increasing its volume which will allow it to pick up the unwanted heat in the evaporator.
- It also controls the flow of refrigerant according to the load on the evaporator.
- It also maintain the desired pressure difference so that the liquid refrigerant vaporizes at desired pressure in the evaporator.
There are three types of refrigerant control devices used in the industry: electronic expansion valves, fixed orifices and float systems.


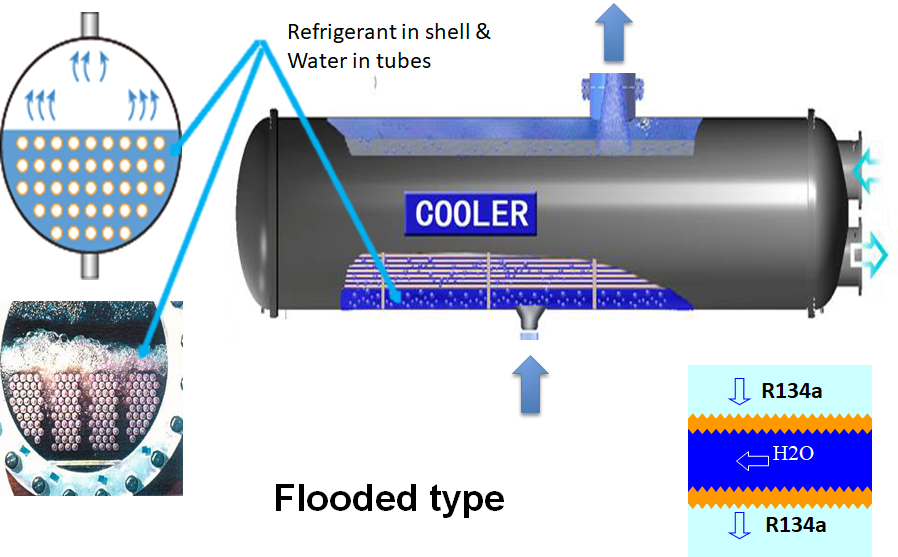
Evaporator:
The purpose of evaporator is to absorb heat from the building/surrounding or the medium which is to be cooled (water) & transfer it to the refrigerant which later send it to the cooling tower & get rejected to the atmosphere. The chilled water than pumped around the building to provide air-conditioning. Evaporator is located between the expansion valve & compressor. The evaporator cools by using the refrigerant’s latent heat of vaporization to absorb heat from the medium being cooled.
The different kind of evaporator available are Direct expansion evaporator, Flooded Evaporator, Falling film evaporator.
By virtue of its structure Shell& tube, tube in Tube & plate type heat exchangers are popular. Plate type are ideal for small to medium loads while shell and tube are ideal for medium to large loads.
In shell & tube evaporator water is pumped through the copper tubes & liquid refrigerant is fed in the shell made of carbon steel.
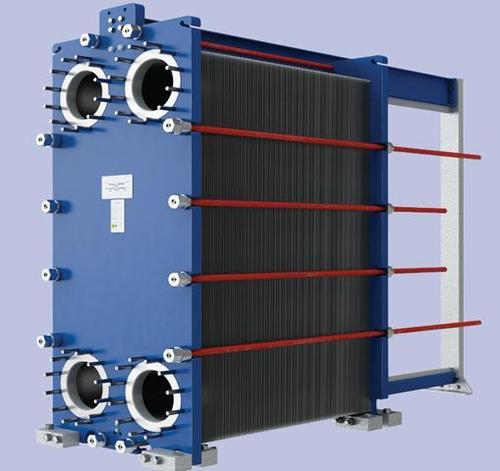
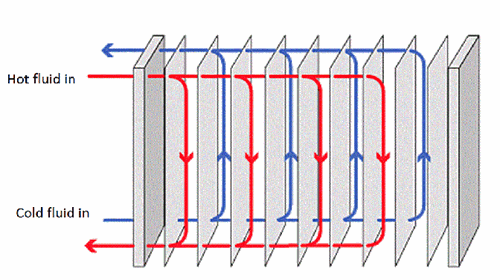
Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger: Their typical construction materials consists of stainless steel plates held together with a copper based brazing material. Water & refrigerant circulates in alternating plates.
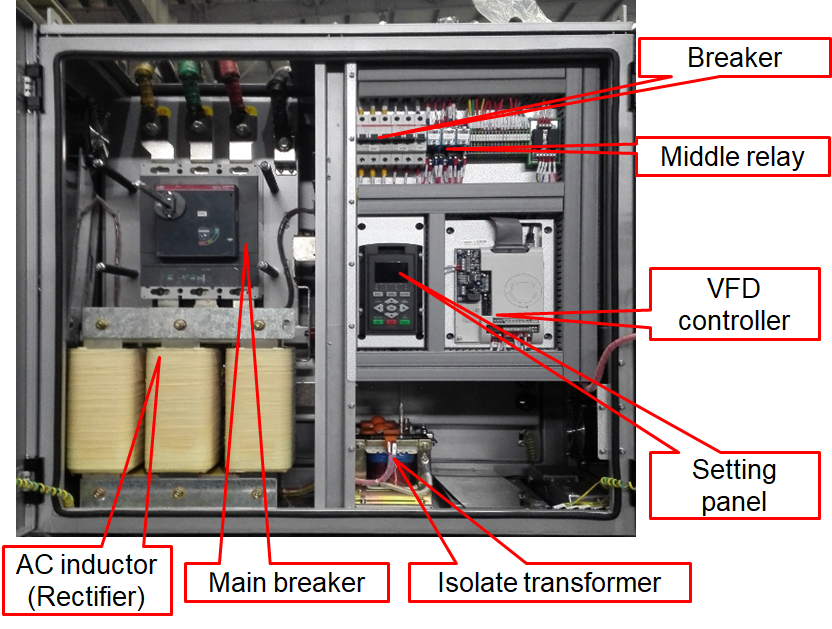
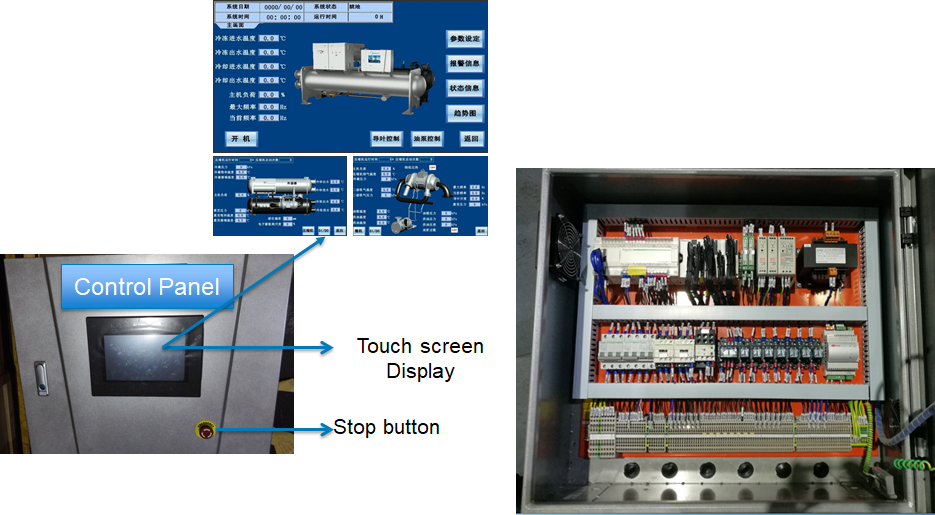
Control Panel:
The perfect operating and control system of chiller integrates a series of control and monitoring functions including intelligent operations, safety protection and interlocking control to achieve reliable start, high efficiency operations and internal control of chiller. It is mounted directly on the chiller.
It also can communicate with the user’s PC and enable the remote control of start/stop and the cooling system. More than 30 protection features are used to make the chiller’s operations secure and reliable. The latest failure reports can be recorded for querying. Control unit will generate alarms for the engineering teams and safely shut the system down to prevent damage to the unit.
Power Supply panel:
It is mounted on the chiller or plant rooms. It is responsible of electrical power supply & management & mainly consists of power supply terminals, circuit breakers, fuses & relays for protecting the compressor, thermal cutout switches to protect fans, starter equipment etc.