What is Fouling in Heat exchangers?
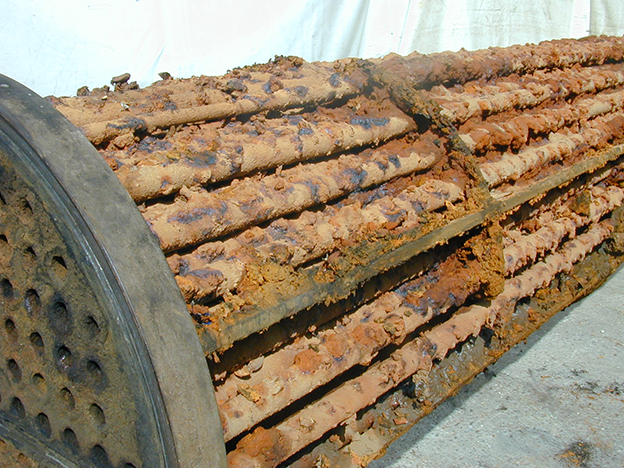

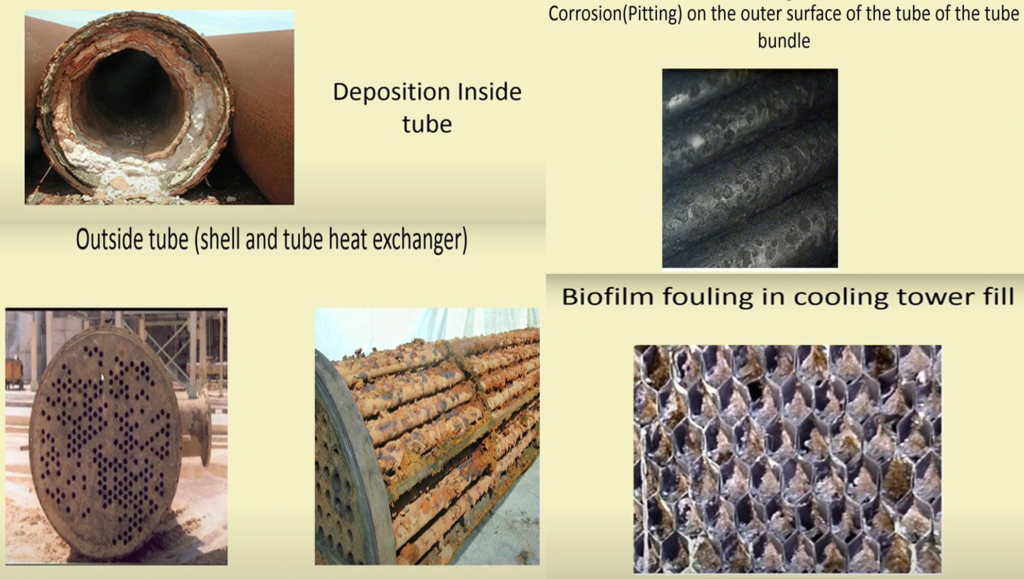
- Accumulation of undesirable materials(deposits) on Heat exchanger surfaces.
- Undesirable materials may be crystals, polymers, inorganic salts, biological growth, corrosion products etc.
- This Phenomena of rust formation & deposition of fluid impurities is called fouling.
- Depends significantly on the operating conditions.
Effects Of Fouling
- Affects Heat Transfer & Flow.
- The deposits represents the additional resistance to heat flow.
- May promote corrosion & may results in failure of some heat exchangers.
- Reduction in thermal performance (heat transfer) & increase fluid pressure drop.
- If h is the heat transfer Δp is the pressure drop & D is the dia of heat exchanger tube than
h ∝ Dh & Δp ∝ 1/D3h
Fouling accumulation results in decrease in cross sectional area of water flow passage which in return decrease heat transfer & increased pressure drop.
Fouling Mechanisms
- Precipitation or crystallization fouling: Depending on the chemical properties & temperature of the fluid this can occur.
- Particulate fouling: This is when particles contained within the fluid settle out onto the surface when the fluid velocity falls below a critical level. When this type of fouling occurs it is normally removed by mechanical brushing processes.
- Chemical reaction fouling: when chemical changes within the fluid cause a fouling layer to be deposited onto the tube surface. A common example of this phenomenon is scaling in a kettle or boiler caused by “hardness” salts depositing onto the heating elements as the solubility of the salts reduce with increasing temperature.
- Corrosion fouling: This is when a layer of corrosion products build up on the surfaces of the tube forming an extra layer of, usually, high thermal resistance material. By careful choice of materials of construction the effects can be minimized as a wide range of corrosion resistant materials based on stainless steel and other nickel-based alloys are now available to the heat exchanger manufacturer.
- Biological fouling: This is caused by the growth of organisms within the fluid which deposit out onto the surfaces of the heat exchanger. When this type of fouling occurs it is normally removed by either chemical treatment or mechanical brushing processes.
- Freezing (solidification fouling):This occurs when the temperature of fluid at heat transfer surface falls below freezing point. A formation of ice crystals again will choke the passage & affects heat transfer.
Examples of Fouling
Fouling Factor Mathematical representation
The fouling factor represents the theoretical thermal resistance to heat flow introduced by fouling material.
Usually denoted by “Rf“
For any Heat exchanger
Rf = 0 …. For new heat exchanger
Rf ∝ Time in use of HE
Rf ∝ Temperature of fluid used
Rf ∝ 1/ Velocity of fluid

The expression for fouling is depends upon the surface area. More the surface are more will be the fouling material deposition. Hence,
Resistance added by foul is given by
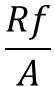
where A is the surface area of tube.
The fouling can be Outside as well as inside of the tube.
For any heat exchanger ,the total resistance to heat transfer can be written as:


From below equation we can find value of U:

this value we can put in first equation to get “RfT“.
The Value of fouling factor ranges between 0.0001 to 0.001
Unit of fouling factor is:

Commonly used Fouling Factor for Chillers:
| Sr. No | h-ft2 – 0 F/BTU | m2–0C/kw | m2–0C/w | m2-h-0C/Kcal |
| 1 | 0.0001 | 0.0176 | 0.0000176 | 0.0000205 |
| 2 | 0.00025 | 0.044 | 0.000044 | 0.0000512 |
| 3 | 0.0005 | 0.0881 | 0.0000881 | 0.000102 |
| 4 | 0.00075 | 0.132 | 0.000132 | 0.000154 |
| 5 | 0.001 | 0.176 | 0.000176 | 0.000205 |
The fouling factors to be used in the design of heat exchangers are normally specified by the client based on their experience of running the plant or process.
They are often overstated by the end user in an attempt to minimize the frequency of cleaning. In reality, if the wrong fouling factor is used, cleaning may actually be required more frequently.
1 thought on “Fouling Factor & Its Significance”